
Apollo 17 (AS-512)
The Last Manned Lunar Landing
The successful Apollo 17 manned lunar landing mission was the last in a series of three J-type missions planned for the Apollo Program. The J-type missions have been characterized by extended hardware capability, by a scientific payload larger than the previous G- and H-series missions and by use of a battery powered lunar rover vehicle (LRV).
As a result of these additions, the Apollo 17 mission had a duration of 12.6 days, and a time on the lunar surface of 75 hr with a total surface traverse distance of approximately 35 km.
 Apollo 17 was manned by Eugene A. Cernan, commander, Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Cernan previously flew in space aboard Gemini IX and Apollo 10, while Apollo 17 was the first flight into space for Evans and Schmitt. Schmitt was the only professional geologist to go to the Moon.
Apollo 17 was manned by Eugene A. Cernan, commander, Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. Cernan previously flew in space aboard Gemini IX and Apollo 10, while Apollo 17 was the first flight into space for Evans and Schmitt. Schmitt was the only professional geologist to go to the Moon.
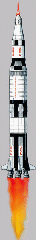 The Saturn V carrying Apollo 17 was launched from NASA John F. Kennedy Space Center at 05:33:00 GMT on December 7, 1972 (11:33:00 p.m. CST on December 6, 1972).
The landing site was on the southeastern rim of Mare Serenitatis in a dark deposit between massif units of the southwestern Montes Taurus.
Scientific objectives included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting inflight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast.
Lunar orbit insertion, executed at 19:47:23 GMT on December 10, placed the spacecraft into a lunar orbit of 170.0 by 52.6 nautical miles. Following a nominal descent sequence, the spacecraft landed at 19:54:57 GMT on December 11 in a valley at Taurus-Littrow, less than 200 m from the preferred landing point.
The first lunar surface EVA began at 23:54:49 GMT on December 11, with Cernan stepping out of the spacecraft at 00:01:00 GMT on December 12. Deployment of the Apollo lunar-surface experiments package (ALSEP) and the cosmic ray experiment took place during EVA-1. Duration of this EVA was 7 hr 12 min.
The second EVA began at 23:28:06 GMT on December 12. Using the LRV, samples from Nansen Crater, Lara Crater and others were collected. Traverses, core samples and trenches were dug at different stations.
This EVA lasted 7 hr 37 min.
The Saturn V carrying Apollo 17 was launched from NASA John F. Kennedy Space Center at 05:33:00 GMT on December 7, 1972 (11:33:00 p.m. CST on December 6, 1972).
The landing site was on the southeastern rim of Mare Serenitatis in a dark deposit between massif units of the southwestern Montes Taurus.
Scientific objectives included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting inflight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast.
Lunar orbit insertion, executed at 19:47:23 GMT on December 10, placed the spacecraft into a lunar orbit of 170.0 by 52.6 nautical miles. Following a nominal descent sequence, the spacecraft landed at 19:54:57 GMT on December 11 in a valley at Taurus-Littrow, less than 200 m from the preferred landing point.
The first lunar surface EVA began at 23:54:49 GMT on December 11, with Cernan stepping out of the spacecraft at 00:01:00 GMT on December 12. Deployment of the Apollo lunar-surface experiments package (ALSEP) and the cosmic ray experiment took place during EVA-1. Duration of this EVA was 7 hr 12 min.
The second EVA began at 23:28:06 GMT on December 12. Using the LRV, samples from Nansen Crater, Lara Crater and others were collected. Traverses, core samples and trenches were dug at different stations.
This EVA lasted 7 hr 37 min.
 During EVA-3, sampling stops were made and traverse gravimeter measurements were taken. Additional explosive packages for the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment were also deployed. One of the final science activities was the retrieval of the neutron flux probe from the deep drill core hole. The third EVA ended at 05:40:56 GMT on December 14.
The LM ascent stage lifted off the Moon at 22:54:37 GMT on December 14. Lift-off and ascent were recorded by the ground-commanded television assembly on the LRV. After docking with the CSM, the ascent stage was sent back to the lunar surface. Its impact was recorded by the four Apollo 17 geophones and by each ALSEP at the Apollo
12,
14,
15 and
16 landing sites.
During EVA-3, sampling stops were made and traverse gravimeter measurements were taken. Additional explosive packages for the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment were also deployed. One of the final science activities was the retrieval of the neutron flux probe from the deep drill core hole. The third EVA ended at 05:40:56 GMT on December 14.
The LM ascent stage lifted off the Moon at 22:54:37 GMT on December 14. Lift-off and ascent were recorded by the ground-commanded television assembly on the LRV. After docking with the CSM, the ascent stage was sent back to the lunar surface. Its impact was recorded by the four Apollo 17 geophones and by each ALSEP at the Apollo
12,
14,
15 and
16 landing sites.
From NASA SP-330, Apollo 17 Preliminary Science Report and Apollo 17 Press Kit, Release No: 72-220K
 Factoids
Factoids
-
- Lunar Module - Challenger ; Command and Service Module - America.
- Launched from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39A.
- Third for Cernan (Gemini IX, Apollo 10), first for Evans and Schmitt.
- The backup crew members were John W. Young, commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Charles M. Duke, lunar module pilot.
- First Geologist on lunar surface.
- Longest LRV traversed on a single EVA.
- Greatest amount of lunar samples returned to Earth.
- Third mission with a lunar roving vehicle (LRV) that could transport two astronauts. The LRV could also carry tools, scientific equipment, communications gear, and lunar samples.
- Mission duration: 301 hr 51 min 59 sec.
Images from mission
Standard figures from Press Release package.
Michael J. Tuttle, June 28, 1995






 Main Apollo page
Main Apollo page